Can a toothache cause a headache
The Surprising Connection Between Tooth Pain and Headaches
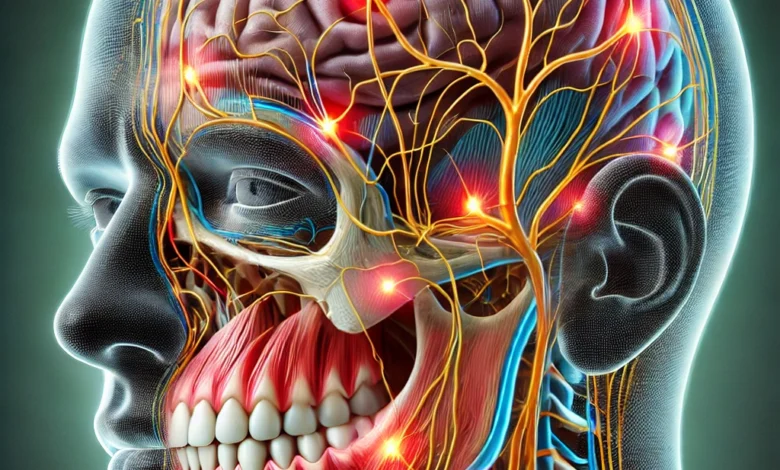
Understanding the Connection Between Toothaches and Headaches (Can a toothache cause a headache)
Experiencing a toothache is never pleasant, and neither is dealing with a headache. But what if these two ailments are connected? Can a toothache cause a headache? Understanding the relationship between dental pain and headaches involves delving into our facial anatomy and recognizing how pain can travel along shared pathways.
Shared Neural Pathways: The Trigeminal Nerve
The key to understanding the connection between toothaches and headaches lies in the trigeminal nerve. This nerve is one of the primary conduits for sensation in the face, including the teeth, gums, jaw, and parts of the head. When a tooth becomes infected or inflamed, the resulting pain can stimulate the trigeminal nerve. This stimulation doesn’t always confine the pain to the tooth; it can radiate to other areas served by the nerve, including regions of the head, leading to headaches.
Dental Conditions That May Lead to Headaches
Several dental conditions can contribute to headaches due to the complex network of nerves and muscles connecting the mouth, jaw, and head. Here’s a breakdown:
-
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ or TMD):
- The temporomandibular joint connects the jaw to the skull. Dysfunction in this joint can lead to jaw pain, tension headaches, and even migraines. Common causes include teeth grinding, jaw clenching, or arthritis.
-
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding):
- Chronic grinding or clenching of teeth, often during sleep, puts pressure on the jaw and surrounding muscles, leading to tension headaches and facial pain.
-
Malocclusion (Misaligned Bite):
- An improper bite alignment can strain the jaw muscles and lead to headaches due to overuse and tension in the facial muscles.
-
Tooth Infections or Abscesses:
- An untreated tooth infection or abscess can cause localized pain that radiates to the head, mimicking a headache.
-
Cavities and Tooth Decay:
- Severe cavities that reach the nerve endings can cause referred pain that spreads to the head and causes headaches.
-
Sinus Infections and Dental Pain:
- Infections in the upper teeth can sometimes affect the sinuses, leading to sinus headaches.
-
Wisdom Tooth Impaction:
- Impacted wisdom teeth can cause jaw pain and inflammation that radiates to the head and triggers headaches.
-
Poor Posture and Jaw Alignment Issues:
- Poor posture, especially forward head posture, can stress the neck and jaw muscles, leading to tension headaches.
If you suspect a dental issue is causing your headaches, consulting a dentist or a specialist in orofacial pain can help identify the root cause and provide appropriate treatment.
Dental Abscesses:
An infection at the root of a tooth, often referred to as a dental abscess, can result in significant pain and discomfort. The infection typically occurs when bacteria enter the tooth through a cavity or crack and reach the pulp, which is the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. If left untreated, the infection can spread, causing severe pain, swelling, and even damage to the surrounding bone and tissues.
The pain from a tooth infection can sometimes radiate beyond the tooth itself, as it may irritate the trigeminal nerve, one of the primary nerves responsible for sensation in the face, including the teeth, gums, and jaw. The trigeminal nerve has three branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves. When the root infection inflames or pressures the nerve, it can cause referred pain, which may lead to headaches, facial pain, or discomfort in other parts of the head and neck.
Headaches associated with a tooth infection are usually dull, aching, and can worsen when pressure is applied to the affected tooth or jaw. If the infection progresses and is not treated in time, it can also lead to more serious health complications, including the spread of the infection to other areas like the jaw, neck, or even the brain.
Therefore, it is crucial to seek dental treatment as soon as possible if you experience persistent tooth pain, sensitivity, swelling, or headaches. Timely treatment, such as a root canal or tooth extraction, can help eliminate the infection and relieve both the localized tooth pain and any secondary symptoms, including headaches.
Cavities and Tooth Decay:
Untreated cavities can progress to affect deeper structures of the tooth, causing pain that may radiate to the head.
Impacted Wisdom Teeth:
When wisdom teeth don’t emerge properly, they can cause pressure and pain in the jaw, which may extend to headache-like symptoms.
Muscular Factors: Bruxism and TMJ Disorders
Beyond direct nerve stimulation, certain muscular activities related to dental health can contribute to headaches:
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding):
Grinding teeth, often unconsciously during sleep, can strain jaw muscles. This strain can lead to tension headaches, characterized by a dull, aching pain around the temples or forehead.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
The TMJ connects the jawbone to the skull. Disorders in this joint can cause pain in the jaw and head regions, manifesting as headaches. Symptoms may include jaw pain, clicking sounds, and headaches.
Sinus and Dental Pain Overlap
The proximity of the sinuses to dental structures can lead to overlapping pain sensations:
Sinusitis:
Infections or inflammation of the sinuses can cause facial pain, sometimes mistaken for toothache. Conversely, dental infections can spread to the sinuses, leading to sinusitis. Distinguishing between dental pain and sinus-related pain is crucial for appropriate treatment.
Recognizing Symptoms Indicative of a Link
Identifying when a toothache may be causing a headache involves:
Pain Location:
If both tooth pain and headache occur on the same side of the face, there may be a connection.
Pain Characteristics:
Dental-related headaches often present as dull, aching pains around the temples or forehead.
Duration and Timing:
Persistent tooth pain accompanied by headaches warrants professional evaluation.
Diagnostic Approaches and Treatment Options
When experiencing both tooth and head pain, it’s essential to consult healthcare professionals:
Dental Evaluation:
A dentist can assess for infections, cavities, or TMJ disorders contributing to pain.
Medical Assessment:
A physician can evaluate for sinus issues or other medical conditions causing headaches.
Treatment may involve:
Addressing Dental Issues:
Treating infections, performing necessary dental procedures, or managing TMJ disorders.
Managing Headaches:
Utilizing pain relief strategies, stress management techniques, or physical therapy for muscular issues.
Preventive Strategies
Maintaining good oral and overall health can reduce the risk of both toothaches and headaches:
-
Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing regularly to prevent cavities and gum disease.
-
Stress Management: Engaging in relaxation techniques to reduce the risk of bruxism and associated headaches.
-
Regular Check-ups: Routine dental and medical examinations can help identify and address issues before they lead to pain.
The relationship between toothaches and headaches is complex, involving shared neural pathways, muscular factors, and anatomical proximity. Understanding this connection highlights the importance of comprehensive healthcare, addressing both dental and medical aspects to alleviate pain effectively. If you experience concurrent tooth and head pain, seeking professional evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Visit here to read more important posts about health and fitness on our website. crazzythings.com



